Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
About me
This is a page not in th emain menu
Published:
This post will show up by default. To disable scheduling of future posts, edit config.yml and set future: false.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Single pion production (SPP) induced by neutrino-nucleon scattering is one of the processes used to measure the neutrino oscillation parameters. We have proposed several improvements in the theoretical description of the SPP. Inpapers Phys. Rev. D77, 053001 and Phys. Rev. D77, 053003, a new scheme for modeling resonance form factors in the Rein-Sehgal model and an algorithm for implementing the lepton mass effects were proposed. Several experimental Monte Carlo generators, including NEUT implemented our results. In Phys. Rev. D 80, 093001, we studied the ANL and BNL data for SPP. For the first time, it was shown that both data sets are consistent, contrary to what was claimed before in previous analyses. In Phys.Rev. D80, 093001, and Phys. Rev. D90, 093001, we obtained new parametrizations for the weak nucleon-Delta excitation transition matrix element.

We adapted and developed the Bayesian neural network (BNN) approach to study nucleon’s electroweak internal structure. This method allows reducing the dependence of analysis results on model assumptions. In paper JHEP 09, 053 (2010), we obtained a new parametrization of the proton and neutron’s electromagnetic form factors, and in Phys.Rev.C 99 (2019), 025204 an analogous study was done for the axial form factor. The latter paper showed that neutrino-deuteron scattering data do not contain enough information to study non-dipole corrections. In papers Phys. Rev. C84, 034314; J. Phys. G42, 034019, we studied the two-photon exchange effect. In paper Phys. Rev. C88, 065205 results of the BNN approach were compared to the quantum field theoretical computations. Finally, in Phys. Rev. C90, 054334, we used the Bayesian objective algorithm to calculate the charged proton radius. In addition to the papers’ results, BNN C++ library (written from scratch by K. Graczyk and C. Juszczak) resulted from this study.

In paper Sci. Rep 10, 21488 (2020), together with Maciej Matyka we proved the deep learning systems’ ability to encode information about porous media fluid dynamics. We adapted the convolutional neural networks (CNN) to relate initial configurations of obstacles, represented by a picture, with three fundamental quantities in the porous media: porosity, permeability, and tortuosity. We showed that our CNN reproduces the values of porosity, permeability, and tortuosity with reasonable accuracy. 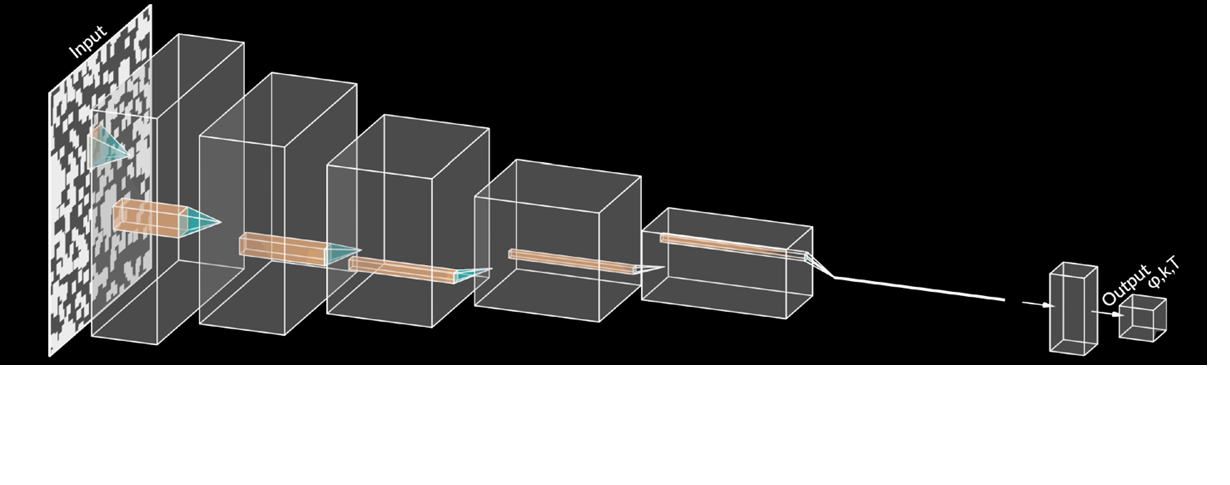
The project aims to find the superalgebra structure that describes intrinsic symmetry. We start from the Poincare and Anti-de Sitter structures. We extend the primary structures by exploiting the so-called resonant construction by adding additional symmetry generators. We analyze millions of superalgebra candidates to find the generator configurations that obey the Poincare or AdS-like super structures pattern. The successful superalgebra structures must satisfy the Jacobi identities.
The main goal of the project was to study the information content of the polarization asymmetries in:
The project was done with Beata Kowal.
Target spin asymmetry and double and triple spin asymmetries have been studied for the first time for the QE scattering. We showed that double spin asymmetries and triple spin asymmetry contain information about the axial content of the nucleon and are perfect observables for measuring the axial form factor of the nucleon.
One of the problems in modeling the SPP in neutrino-nucleon interactions is a proper description of the resonant (RES) and non-resonant (NR) contribution to the neutrino scattering cross-sections. We showed that the target spin asymmetries and recoil nucleon polarization contain nontrivial information about the interference of resonant and non-resonant amplitudes. In particular, we showed that measurement of the target spin asymmetries might carry out the information about the relative phase between RES and NR amplitudes as well as the NR amplitudes. We also studied the sensitivity of spin asymmetries on the parameters of the N-Delta(1232) weak transition model. 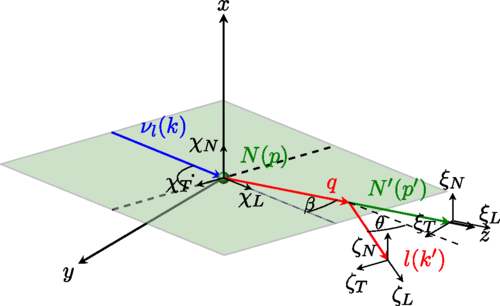
Published in Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics , 2003
Recommended citation: F. Arneodo et al., Nucl.Instrum.Meth.A 508, 287 (2003) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9002(03)01508-0
Published in The European Physical Journal C, 2003
The algebraic solution of RPA equations nucleon re-interactions in the case of quasi elastic charged current neutrino - nucleus scattering is presented. Abelian algebra of matrices allows to extract four independent corrections to cross section separatly.Results of numerical computations are shown.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Eur.Phys.J.C 31, 177 (2003) https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s2003-01338-6
Published in arxiv, 2004
Numerical computations of cross sections for quasielastic charge current scattering of neutrino on Oxygen, Argon and Iron in Local Density Approximation (LDA) are presented. We consider processes for a few GeV neutrino energy. We include corrections from nucleon re-interaction in nucleus described by relativistic Random Phase Approximation (RPA). We adopt the relativistic Fermi gas model of nucleus with and without taking into account the effective mass of nucleons.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, nucl-th/0401053 https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.10304
Published in Nuclear Physics A, 2005
The quasielastic charged-current (CC) tau neutrino(antineutrino)–nucleus scattering is considered. The dependence of tau polarization on nuclear-structure effects is discussed in detail. The description of the nucleus is based on the mean-field theory (MFT). The ground state of nucleus is described using the relativistic Fermi gas model (FG). The effective mass is introduced as well as the ring random phase approximation (RPA) effects are taken into account in the framework of relativistic meson–nucleon model. The local density approximation (LDA) is used for the argon nucleus, having in mind possible application to the ICARUS experiment. The discussion concentrates on the threshold region where the can be unpolarized and the nuclear effects play an important role.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Nucl.Phys.A 748, 313 (2005) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2004.10.029
Published in Nuclear Physics B - Proceedings Supplements, Part of Proceedings, 3rd International Workshop on Neutrino-nucleus interactions in the few GeV region (NUINT 04) : Assergi, Italy, March 17-21, 2004, 2005
Numerical results for the degree of polarization of tau- produced in (CC) neutrino-nucleon Deep Inelastic Scattering (DIS) are presented. Calculations are done in the threshold region, where the tau- scattered by the small angles and can be partially polarized. The cross sections and polarization are calculated by using the GRV98 parton distributions functions (PDFs) and the GRV98 with modifications of A. Bodek at.al. Nucl. Phys. B Proc.(Suppl) 112 (2002) 70.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Nucl.Phys.B Proc.Suppl. 139,150 (2005) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysbps.2004.11.230
Published in Nuclear Physics B - Proceedings Supplements, Part of Proceedings, 3rd International Workshop on Neutrino-nucleus interactions in the few GeV region (NUINT 04) : Assergi, Italy, March 17-21, 2004, 2005
We constructed a new Monte Carlo generator of events for neutrino CC single pion production on free nucleon targets. The code uses dynamical models of the DIS with the PDFs modified according to the recent JLab data and of the Delta excitation. A comparison with experimental data was done in three channels for the total cross sections and for the distributions of events in invariant hadronic mass.
Recommended citation: Jan T. Sobczyk, Jarosław A. Nowak, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Nucl.Phys.B Proc.Suppl. 139, 266 (2005) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysbps.2004.11.218
Published in Part of Nuclear effects in neutrino interactions. Proceedings, 20th Max Born Symposium, Wroclaw, Poland, December 7-10, 2005, 2006
An analysis of the Rein-Sehgal model in the context of the quark–hadron duality hypothesis is presented. The resonance region structure functions reconstructed from the Rein–Sehgal model at different values of QRES2Q^2{\rm RES}QRES2 are compared with the DIS structure functions calculated at higher QDIS2Q^2{\rm DIS}QDIS2. The ratios of corresponding integrals in the Nachtman variable are also calculated and presented as functions of QRES2Q^{2}{\rm RES}QRES2. The obtained functions are approximately flat for QRES2>0.5Q^2{\rm RES}>0.5QRES2>0.5\,GeV2^22 but the quark–hadron duality is not observed.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Acta Phys.Polon.B 37, 2321 (2006) https://www.actaphys.uj.edu.pl/index_n.php?I=R&V=37&N=8#2321
Published in Nuclear Physics B - Proceedings Supplements, Part of Proceedings, 4th International Workshop on Neutrino nucleus interactions in the few GeV region (NUINT 05) : Okayama, Japan, September 26-29, 2005, 2006
Quark-hadron duality in neutrino-nucleon reactions is investigated under the assumption that cross sections in the resonance region are given by the Rein-Sehgal model. The quantitative analysis of the duality is done by means of appropriate integrals of the structure functions in the Nachtmann variable. We conclude that with the definition of the resonance region W∈(M+mπ,2W\in (M+m_{\pi}, 2W∈(M+mπ,2 GeV) the duality holds for neutrino-proton reaction F2F_2F2 structure function for Q2∈(0.5,3)Q^2\in (0.5, 3)Q2∈(0.5,3) GeV2^22 and it is absent for neutrino-neutron reaction.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Cezary Juszczak, Jan T. Sobczyk, Nucl.Phys.B Proc.Suppl. 159, 241 (2006) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysbps.2006.08.043
Published in Nuclear Physics A, 2007
The quark-hadron duality in CC and NC neutrino interactions is discussed under assumptions that single pion production is described accurately by the Rein-Sehgal model and that it allows reconstruction of the inclusive cross section in the resonance region. The duality is measured by means of integrals of structure functions in the Nachtmann variable for Q2<3Q^2<3Q2<3 GeV2^22. The results depend on the precision with which contributions from single pion production channels in the overall cross sections are known. Several approaches to evaluate them are compared. The duality is predicted to be seen for proton target reactions and to be absent for neutron and isoscalar targets. Two-component duality between resonant and valence quark contributions to structure functions is also investigated.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk and Jan T. Sobczyk, Nucl.Phys.A 781, 227 (2007) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2006.10.036
Published in Proceedings, 5th International Workshop on Neutrino-Nucleus Interactions in the Few GeV Region (NUINT 07) : Batavia, USA, May 30-June 3, 2007, 2007
New vector and axial form factors in the Rein‐Sehgal model are proposed. The vector part is constructed after experimental fits of the helicity amplitudes for electroproduction of Δ(1232) resonance. The axial part is calculated after 𝑄2 distribution of events in the ANL experiment.
Recommended citation: K. Graczyk, AIP Conference Proceedings 967, 205 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2834479
Published in Physical Review D, 2008
Vector and axial form factors in the quark resonance model are analyzed with a combination of theoretical and phenomenological arguments. The new form of form factors is deduced from Δ(1232) excitation models and available data. The vector part is shown to agree with the resonant contribution to electron-proton inclusive F2 data. The axial part is obtained by finding a simultaneous fit to ANL and BNL dσ/dQ2 neutrino scattering data. The best fit corresponds to CA5(0)=0.88 in the Rarita-Schwinger formalism.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk and Jan T. Sobczyk, Phys. Rev. D 77, 053001 (2008) https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.77.053001
Published in Physical Review D, 2008
Different approaches to take into account nonzero lepton mass effects in the Rein-Sehgal model are compared. Modification of the axial current due to a pion pole term is included, and it is shown that it leads to large reduction of the antineutrino cross section and a change of the shape of dσ/dQ2.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk and Jan T. Sobczyk, Phys. Rev. D 77, 053003 (2008) https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.77.053003
Published in Proceedings Contribution to 27th International Workshop on Nuclear Theory (IWNT 2008), 23-28 June 2008. Rila Mountains, Bulgaria, 2008
Single pion production in neutrino-nucleon scattering is discussed. The neutrino energies characteristic for T2K project are considered. Two new parameterizations of C_5^A axial form factor are proposed. Both of them are obtained in simultaneous fit to ANL and BNL data. One of them (which fits better to BNL data) leads to d\sigma/dQ^2 differential cross section which is significantly reduced at low Q^2.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, arXiv:0810.1247 https://arxiv.org/abs/0810.1247
Published in Proceedings, Europhysics Conference on High energy physics (EPS-HEP 2009) : Cracow, Poland, July 16-22, 2009, 2009
This talk presents some of the results of the re-analysis of [Graczyk et al.] of the bubble chamber data for single pion production induced by neutrino scattering off deuteron. It is shown that ANL and BNL data are statistically consistent. The validity of the Adler relations (between P33(1232) resonance axial form factors) is also investigated.
Recommended citation: K. Graczyk, PoS EPS-HEP2009, 286 (2009). https://doi.org/10.22323/1.084.0286
Published in Acta Physica Polonica B, Part of Proceedings of 45th Karpacz Winter School in Theoretical Physics: Neutrino interactions: from theory to Monte Carlo simulations. Ladek-Zdroj, Poland, February 2-11, 2009,, 2009
C5A(Q2) axial form factor is extracted from the ANL neutrino–deuteron scattering data with deuteron structure effects taken into consideration. The best fit of the CA5(Q2) axial form factor is obtained assuming dipole parametrization with C5A(0)=1.13±0.15 and MA=0.94±0.08 GeV.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, D. Kiełczewska, J. T. Sobczyk, Acta Phys. Pol. B 40, 2565 (2009) https://www.actaphys.uj.edu.pl/R/40/9/2565
Published in Joural of Physics G, 2009
We present predictions for the value of the cross section ratio σ(e+p → e+p)/σ(e−p → e−p), determined from our fit of the elastic ep cross section and polarization data. In this fit, we took into account the phenomenological two-photon exchange dispersive correction. The cross section ratios which are expected to be measured by the VEPP-3 experiment are computed. The kinematical region which will be covered by the E04-116 JLab experiment is also considered. It is shown that for both experiments the predicted cross section ratios deviate from unity by more than 3σ.
Recommended citation: W. M. Alberico, S. M. Bilenky, C Giunti, and K. M. Graczyk, J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 36 115009 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1088/0954-3899/36/11/115009
Published in Physical Review C, 2009
Electromagnetic form factors of proton and neutron, obtained from a new fit of data, are presented. The proton form factors are obtained from a simultaneous fit to the ratio μpGEp/GMp determined from polarization transfer measurements and to ep elastic cross section data. Phenomenological two-photon exchange corrections are taken into account. The present fit for protons was performed in the kinematical region Q2∈(0,6) GeV2. For both protons and neutrons we use the latest available data. For all form factors, the uncertainties and correlations of form factor parameters are investigated with the χ2 method.
Recommended citation: W. M. Alberico, S. M. Bilenky, C. Giunti, and K. M. Graczyk, Phys. Rev. C 79, 065204 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.79.065204
Published in Physical Review D, 2009
A careful reanalysis of both Argonne National Laboratory and Brookhaven National Laboratory data for weak single pion production is done. We consider deuteron nuclear effects and normalization (flux) uncertainties in both experiments. We demonstrate that these two sets of data are in good agreement. For the dipole parametrization of CA5(Q2), we obtain CA5(0)=1.19±0.08, MA=0.94±0.03 GeV. As an application we present the discussion of the uncertainty of the neutral current 1π0 production cross section, important for the T2K neutrino oscillation experiment.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, D. Kiełczewska, P. Przewłocki, and J. T. Sobczyk, Phys.Rev.D 80, 093001 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.80.093001
Published in Proceedings, 11th International Workshop on Neutrino Factories, Superbeams and Betabeams (NuFact09) : Chicago, Illinois, July 20-25,2009, 2010
Quark‐hadron (QH) duality in lepton scattering off nucleons is studied with the resonance quark model. It is shown that in the case of neutrino scattering off an isoscalar target the duality is simultaneously observed for charged and neutral currents xFνN1, FνN2, and xFνN3 weak structure functions. We demonstrate that the QH duality can be a useful property for modeling structure functions in the so‐called resonance region. As an example it is shown that combining relativistic quark model predictions with duality arguments allows a construction of the inclusive resonance Fep2 structure function.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, AIP Conf.Proc. 1222, 1, 238 (2010) https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3399304
Published in Journal of High Energy Physics, 2010
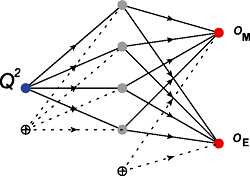
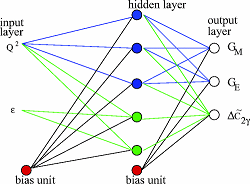
The electromagnetic nucleon form-factors data are studied with artificial feed forward neural networks. As a result the unbiased model-independent form-factor parametrizations are evaluated together with uncertainties. The Bayesian approach for the neural networks is adapted for chi2 error-like function and applied to the data analysis. The sequence of the feed forward neural networks with one hidden layer of units is considered. The given neural network represents a particular form-factor parametrization. The so-called evidence (the measure of how much the data favor given statistical model) is computed with the Bayesian framework and it is used to determine the best form factor parametrization.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Piotr Płoński, Robert Sulej, JHEP 09, 053 (2010) https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP09(2010)053
Published in Physical Review C, 2011
An approach to the extraction of the two-photon exchange (TPE) correction from elastic epepep scattering data is presented. The cross section, polarization transfer (PT), and charge asymmetry data are considered. It is assumed that the TPE correction to the PT data is negligible. The form factors and TPE correcting term are given by one multidimensional function approximated by the feed forward neural network (NN). To find a model-independent approximation the Bayesian framework for the NNs is adapted. A large number of different parametrizations is considered. The most optimal model is indicated by the Bayesian algorithm. The obtained fit of the TPE correction behaves linearly in epsilon but it has a nontrivial Q2 dependence. A strong dependence of the TPE fit on the choice of parametrization is observed.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Phys. Rev. C 84, 034314 (2011) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.84.034314
Published in Proceedings, 7th International Workshop on Neutrino-nucleus interactions in the few GeV region (NUINT 11) : Dehradun, India, March 7-11, 2011
A short review of the Rein-Sehgal and isobar models is presented. The attention is focused on the nucleon-(1232) weak transition form-factors. The results of the recent re-analyses of the ANL and BNL bubble chamber neutrino-deuteron scattering data are discussed.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, AIP Conf.Proc. 1405, 1, 134, (2011) https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3661573
Published in Physical Review C, 2013
Results of the analysis of the MiniBooNE experiment data for the neutral current elastic neutrino scattering off the CH2 target with the NuWro Monte Carlo generator are presented. The inclusion in the analysis of the two-body current contribution leads to the axial mass value MA=1.10+0.13−0.15 GeV, consistent with the older evaluations based on the neutrino-deuteron scattering data. The strange quark contribution to the nucleon spin is estimated with the value gsA=−0.4+0.5−0.3.
Recommended citation: Tomasz Golan, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Cezary Juszczak, Jan. T. Sobczyk, Phys.Rev.C 88, 024612 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.88.024612
Published in Physical Review C, 2013
Predictions for the two-photon exchange (TPE) correction to the unpolarized ep elastic cross section, obtained within two different approaches, are confronted and discussed in detail. In the first one the TPE correction is extracted from experimental data by applying the Bayesian neural network statistical framework. In the other the TPE is given by box diagrams, with the nucleon and the P33 resonance as the hadronic intermediate states. Two different form factor parametrizations for both the proton and the P33 resonance are taken into consideration. Proton form factors are obtained from the global fit of the full model (with the TPE correction) to the unpolarized cross-section data. Predictions of the two methods agree well in the intermediate Q2 range of 1–3 GeV2. Above Q2=3 GeV2 the agreement is at the 2σ level. Below Q2=1 GeV2 the consistency between the two approaches is broken. The values of the proton radius extracted within the models are given. In both cases predictions for the VEPP-3 experiment have been obtained and confronted with the preliminary experimental results.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Phys. Rev. C 88, 065205 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.88.065205
Published in Joural of Physics G, 2014
Two-boson exchange (TBE) correction in νn→l−p and ν¯p→l+n reactions is estimated. The TBE contribution is given by Wγ box diagrams. The calculations are performed for 1 GeV neutrinos and for the MiniBooNE and the T2K energy spectra. The TBE correction to the total cross section is of the order of 2–4% (with respect to the Born contribution) in the case of νe and ν¯e and 1–2% in the case of νμ and ν¯μ .
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, Phys.Lett.B 732, 315 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2014.03.065
Published in Physical Review D, 2014
Nucleon→Δ(1232) transition electroweak form factors are discussed in a single pion production model with nonresonant background terms originating from a chiral perturbation theory. Fits to electron-proton scattering F2 as well as neutrino scattering bubble chamber experimental data are performed. Both ν-proton and ν-neutron channel data are discussed in a unified statistical model. A new parametrization of the N→Δ(1232) vector form factors is proposed. In the case of model with deuteron nuclear effects fit to neutrino scattering data gives the axial mass MAΔ=0.85+0.09−0.08 GeV and CA5(0)=1.10+0.15−0.14 in accordance with the Goldberger-Treiman relation. However, the consistency is spoiled when the deuteron effects are omitted; i.e., in this case the fit gives the axial mass MAΔ=0.81+0.09−0.09 GeV and CA5(0)=0.93+0.13−0.13.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Jakub Żmuda, and Jan T. Sobczyk, Phys.Rev.D 90, 9, 093001 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.90.093001
Published in Physical Review C, 2014
The methods of Bayesian statistics are used to extract the value of the proton radius from the elastic ep scattering data in a model-independent way. To achieve that goal a large number of parametrizations (equivalent to neural network schemes) are considered and ranked by their conditional probability P(parametrization given data) instead of using the minimal error criterion. As a result the most probable proton radii values (rpE=0.899±0.003 fm, rpM=0.879±0.007 fm) are obtained and systematic error due to freedom in the choice of parametrization is estimated. Correcting the data for the two-photon-exchange effect leads to smaller differences between the extracted values of rpE and rpM. The results disagree with recent muonic atom measurements.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, C. Juszczak, Phys.Rev.C 90, 054334, 045205 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.90.054334
Published in Joural of Physics G, 2015
The Bayesian approach for the feed-forward neural networks is reviewed. Its potential for usage in hadron physics is discussed. As an example of the application, the study of the two-photon exchange effect is presented. We focus on the model comparison, the estimation of the systematic uncertainties due to the choice of the model and the over-fitting. As an illustration, the predictions of the cross sections ratio ${\rm d}\sigma ({{e}^{+}}p\to {{e}^{+}}p)/{\rm d}\sigma ({{e}^{-}}p\to {{e}^{-}}p)$ are given together with the estimate of the uncertainty due to the parametrization choice.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, C. Juszczak, J.Phys.G 42, 3, 034019 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1088/0954-3899/42/3/034019
Published in Physical Review C, 2015
The first and the third Zemach moments are obtained, ⟨r⟩(2)=1.1108±0.0021 fm and ⟨r3⟩(2)=2.889±0.008 fm3, from the Bayesian analysis of the elastic ep scattering data. The quantitative discussion of the dependence of the results on the parametrization choice is presented and the corresponding systematic uncertainties are estimated—about 0.6% and 1.6% for the first and the third Zemach moments, respectively.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, C. Juszczak, Phys.Rev.C 91, 045205 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.91.045205
Published in AIP, Proceedings, Workshop on Neutrino Interactions, Systematic uncertainties and near detector physics: Session of CETUP* 2014 : Lead/Dead Wood, South Dakota, USA, July 22-31, 2014, 2015
We extend and review our analysis of the nucleon → Δ(1232) transition electroweakform factors from Ref. [1]. New fit of the Δ(1232) vector form factors to electron-proton scattering F2 structure function is introduced as well, leading to results different from the popular parametrization of Ref. [2]. A clear model dependence of the extracted parameters emerges. Fit to neutrino scattering data is performed in all available isospin channels. The resulting axial mass is MAΔ=0.85−0.08+0.09(GeV)and C5A(0)=1.10−0.14+0.15. The latter value is in accordance with Goldberger-Treiman relation as long as the deuteron effects are included.
Recommended citation: Jakub Żmuda, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, AIP Conf.Proc. 1680, 1, 020013 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4931872
Published in Acta Physica Polonica B, Part of Proceedings, 41st International Conference of Theoretical Physics: Matter to the Deepest : Kroczyce, Poland, September 4-8, 2017, 2015
NuWro Monte Carlo generator of events is presented. It is a numerical environment containing all necessary ingredients to simulate interactions of neutrinos with nucleons and nuclei in realistic experimental situation in wide neutrino energy range. It can be used both for data analysis as well as studies of nuclear effects in neutrino interactions. The first results and functionalities of eWro — module of NuWro dedicated to electron–nucleus scattering — are also presented.
Recommended citation: Jakub Żmuda, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Cezary Juszczak, Jan T. Sobczyk, Acta Phys.Polon. B46, 2329 (2015) https://www.actaphys.uj.edu.pl/index_n.php?I=R&V=46&N=11#2329
Published in Acta Physica Polonica B, Part of Proceedings, 41st International Conference of Theoretical Physics: Matter to the Deepest : Kroczyce, Poland, September 4-8, 2017, 2017
This article presents a short review of the single pion production (SPP) in the neutrino–nucleon scattering. The attention is focused on the discussion of the main difficulties in modeling the SPP processes. New physical observables, which may constrain the theoretical models, are proposed.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, B. E. Kowal, Acta Phys.Polon.B48, 2219 (2017) https://www.actaphys.uj.edu.pl/index_n.php?I=R&V=48&N=12#2219
Published in Physical Review D, 2018
Polarization transfer (PT) observables in the single pion production induced by the charged current interaction of the neutrino with the nucleon are examined. The polarization components of the final nucleon and the charged lepton are calculated within two models for the pion production. The predictions are made for neutrino energy of the order of 1 GeV as well as for the T2K energy distribution. It is demonstrated that the PT observables, the degree of polarization and the polarization components of outgoing fermions, are sensitive to assumptions about the nonresonant background model. In particular it is shown that the normal components of the polarization of the outgoing nucleon and the lepton are determined by the interference between the resonant (RES) and nonresonant (NB) amplitudes. Moreover, the sign of the normal component of the polarization of the charged lepton is fixed by the relative sign between the RES and the NB amplitudes.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, B. E. Kowal, Phys.Rev.D 97, 013001 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.97.013001
Published in Neutrino 2018 - XXVIII International Conference on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics, 4–9 June 2018 — Heidelberg, Germany , 2018
Polarization transfer (PT) observables in the single pion production induced by the charged current neutrino-nucleon interaction are examined within two models. The predictions are made for neutrino energy of the order of 1 GeV as well as for the T2K energy flux. It is demonstrated that the PT observables: the degree of polarization and the polarization components of outgoing fermions are sensitive to the details of the nonresonant background model. It is shown that the normal component of the polarization of the outgoing nucleon and the charged lepton are determined by the interference between the resonant (RES) and nonresonant (NB) amplitudes. Moreover, the sign of the normal component of the polarization of the charged lepton is related to the relative sign between the RES and the NB amplitudes. The presentation is based on: Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.1, 013001, and Acta Phys.Polon. B48, 2219 (2017).
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1301015 (2018) https://zenodo.org/record/1301015
Published in Proceedings of student poster session of the VII International Pontecorvo Neutrino Physics School (Prague, Czech Republic, August 20 - September 1, 2017), edited by F. Simkovic, - Dubna: JINR, ISBN 978-5-9530-0484-8, 2019
Two models for the single pion production induced by interactions of the neutrinos with the nucleons are studied. The nonresonant background contribution is a subject of analysis. It is shown that the normal component of the polarization of the charged lepton is sensitive on the nonresonant background contribution. It is also demonstrated that the FORM language can be utilized to evaluate all necessary transition matrix elements and the single pion production cross sections.
Recommended citation: Beata E. Kowal, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Proceedings of student poster session of the VII International Pontecorvo Neutrino Physics School (Prague, Czech Republic, August 20 - September 1, 2017), edited by F. Simkovic, - Dubna: JINR, ISBN 978-5-9530-0484-8 http://theor.jinr.ru/~maw/neutrino17/proceeding_full.pdf
Published in Physical Review D, 2019
The single pion production (SPP) in the charged-current neutrino (antineutrino) scattering off the polarized nucleon is discussed. The spin asymmetry is predicted within two approaches. The spin polarizations of the target nucleon that are longitudinal and perpendicular to the neutrino momentum are considered. It is shown, in several examples, that information about the SPP dynamics coming from the spin asymmetry is complementary to information obtained from measurements of spin averaged cross section. Indeed, the spin asymmetry is sensitive to the nonresonance background description of the SPP model. For the normal polarization of the target, the spin asymmetry is given by the interference between the resonance and the nonresonance contributions.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, B. E. Kowal, Phys. Rev. D 99, 053002 (2019) https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.99.053002
Published in Acta Physica Polonica B, Part of Proceedings, 43rd International Conference of Theoretical Physics: Matter to the Deepest, Recent Developments In Physics Of Fundamental Interactions (MTTD2019) : Chorzów/Katowice, Katowice, Poland, September 1-6, 2019, 1771-1780, 2019
Our recent investigations of the spin asymmetry observables in the charged current inelastic and quasielastic neutrino (antineutrino)–nucleon scattering are reviewed. The spin asymmetry observables contain full information about the structure of the electroweak neutrino–nucleon vertex. Hence, they can be used to constrain the cross-section models for the single-pion production in ν-nucleon scattering and they allow to study the axial content of the nucleon and the second class current contribution to the quasielastic scattering amplitudes.
Recommended citation: K. M. Graczyk, B. E. Kowal, Acta Phys.Polon.B 50, 1771 (2019) https://www.actaphys.uj.edu.pl/index_n.php?I=R&V=50&N=11#1771
Published in Proceedings of Science, Part of Proceedings, 20th International Workshop on Neutrinos from Accelerators (NuFact18) : Blacksburg, VA, USA, August 13-18, 2018, 2019
We have performed the first Bayesian neural-network analysis of neutrino-deuteron scattering data. The nucleon axial form factor has been extracted from quasielastic scattering data collected by the Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) bubble chamber experiment using a model-independent parametrization. The results are in agreement with previous determinations only when the low 0.05<Q2<0.10~GeV2 region is excluded from the analysis. This suggests that corrections from the deuteron structure may play a crucial role at low Q2, although experimental errors in this kinematic region could have also been underestimated. With new and more precise measurements of neutrino-induced quasielastic scattering on hydrogen and deuterium, the present framework would be readily applicable to unravel the axial structure of the nucleon.
Recommended citation: L. Alvarez-Ruso, K. Graczyk, E.S. Sala, PoS NuFACT2018 (2019) 101. https://doi.org/10.22323/1.341.0101
Published in Physical Review C, 2019
The Bayesian approach for feedforward neural networks has been applied to the extraction of the nucleon axial form factor from the neutrino-deuteron-scattering data measured by the Argonne National Laboratory bubble-chamber experiment. This framework allows to perform a model-independent determination of the axial form factor from data. When the low 0.05<Q2<0.10−GeV2 data are included in the analysis, the resulting axial radius disagrees with available determinations. Furthermore, a large sensitivity to the corrections from the deuteron structure is obtained. In turn, when the low-Q2 region is not taken into account with or without deuteron corrections, no significant deviations from previous determinations have been observed. A more accurate determination of the nucleon axial form factor requires new precise measurements of neutrino-induced quasielastic scattering on hydrogen and deuterium.
Recommended citation: L. Alvarez-Ruso, K.M. Graczyk, E.S. Sala, Phys. Rev. C 99, 025204 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.99.025204
Published in Physical Review D, 2020
The work concerns the quasielastic charged current neutrino-neutron and antineutrino-proton interactions. Single, double, and triple spin asymmetries are computed and analyzed. The spin asymmetries are sensitive to the axial form factor of the nucleon. In particular, the target-recoil double spin asymmetry and the lepton-target-recoil triple spin asymmetry depend strongly on the axial form factor of the nucleon. Indeed, the sign and shape of these components depend on the axial mass parameter. All the asymmetries, except the lepton polarization, are observables well suited to study the nonstandard interactions described by the second-class current contribution.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk and Beata E. Kowal, Phys. Rev. D 101, 073002 (2020) https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.101.073002
Published in Scientific Reports, 2020
Convolutional neural networks (CNN) are utilized to encode the relation between initial configurations of obstacles and three fundamental quantities in porous media: porosity (𝜑), permeability (k), and tortuosity (T). The two-dimensional systems with obstacles are considered. The fluid flow through a porous medium is simulated with the lattice Boltzmann method. The analysis has been performed for the systems with 𝜑∈(0.37,0.99) which covers five orders of magnitude a span for permeability 𝑘∈(0.78,2.1×105) and tortuosity 𝑇∈(1.03,2.74). It is shown that the CNNs can be used to predict the porosity, permeability, and tortuosity with good accuracy. With the usage of the CNN models, the relation between T and 𝜑 has been obtained and compared with the empirical estimate.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Maciej Matyka, Sci Rep 10, 21488 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78415-x
Published in Physical Review D, 2021
The work presents the study of the polarization observables in the single pion production (SPP) induced by the interaction of the muon neutrino (antineutrino) with nucleons. The SPP cross sections and spin asymmetries are computed within two phenomenological models. One is based on the nonlinear sigma model [E. Hernandez, J. Nieves, and M. Valverde, Phys. Rev. D 76, 033005 (2007)] and the other has origin in the linear sigma model [G. L. Fogli and G. Nardulli, Nucl. Phys. B160, 116 (1979)]. First, we show that the final nucleon polarization and target spin asymmetries are good observables to obtain information about the C5A axial form factor. Second, we demonstrate that the nucleon polarization and the target spin asymmetries are sensitive to the relative phase between resonance and nonresonance amplitudes. We conclude that the polarization of the final nucleon and the target spin asymmetry are promising observables for testing SPP models, including studies of the axial content of Δ(1232) resonance and unitarization procedures.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Beata E. Kowal, Phys. Rev. D 104, 033005 (2021) https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.104.033005
Published in Scientific Reports, 2022
The statistical properties of the density map (DM) approach to counting microbiological objects on images are studied in detail. The DM is given by U2-Net. Two statistical methods for deep neural networks are utilized: the bootstrap and the Monte Carlo (MC) dropout. The detailed analysis of the uncertainties for the DM predictions leads to a deeper understanding of the DM model s deficiencies. Based on our investigation, we propose a self-normalization module in the network. The improved network model, called Self-Normalized Density Map (SNDM), can correct its output density map by itself to accurately predict the total number of objects in the image. The SNDM architecture outperforms the original model. Moreover, both statistical frameworks – bootstrap and MC dropout – have consistent statistical results for SNDM, which were not observed in the original model.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Jarosław Pawłowski, Sylwia Majchrowska, Tomasz Golan, Sci Rep 12, 10583 (2022) https://rdcu.be/cQbPy
Published in European Physical Journal C, 2022
Considering supergravity theory is a natural step in the development of gravity models. This paper follows the algebraic path and constructs possible extensions of the Poincare and Anti-de-Sitter algebras, which inherit their basic commutation structure. Previously achieved results of this type are fragmentary and show only a limited fraction of possible algebraic realizations. Our paper presents the newly obtained symmetry algebras, evaluated within an efficient pattern-based computational method of generating the so-called resonating algebraic structures. These supersymmetric extensions of algebras, going beyond the Poincare and Anti-de Sitter ones, contain additional bosonic generators $Z_{ab}$ (Lorentz-like), and $U_a$ (translational-like) added to the standard Lorentz generator $J_{ab}$ and translation generator $P_{a}$. Our analysis includes all cases up to two fermionic supercharges, $Q_{\alpha}$ and $Y_{\alpha}$. The delivered plethora of superalgebras includes few past results and offers a vastness of new examples. The list of the cases is complete and contains all superalgebras up to two of Lorentz-like, translation-like, and supercharge-like generators $(JP+Q)+(ZU+Y)=JPZU+QY$. In the latter class, among $667$ founded superalgebras, the $264$ are suitable for direct supergravity construction. For each of them, one can construct a unique supergravity model defined by the Lagrangian. As an example, we consider one of the algebra configurations and provide its Lagrangian realization.
Recommended citation: Remigiusz Durka, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Eur. Phys. J. C 82, 254 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-022-10156-9
Published in Physics Letters B, 2022
We present new superalgebra for N=2 D=3,4 supergravity theory endowed with the U(1) generator. The superalgebra is rooted in the so-called Soroka-Soroka algebra and spanned by the Lorentz Jab and Lorentz-like Zab, translation Pa and T generators, as well as two supercharges QIα. We construct a corresponding 3D Chern-Simons supergravity realization of the superalgebra and discuss its relevance.
Recommended citation: Remigiusz Durka, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Phys. Lett. B 833, 137366 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2022.137366
Published in Acta Physica Polonica B, Proceedings, Contribution to the proceedings of The 8th Conference of the Polish Society on Relativity 2022, Warsaw (Poland), 2023
Applying an efficient pattern-based computational method of generating the so-called resonating algebraic structures results in a broad class of the new Lie (super)algebras. Those structures inherit the AdS base (anti) commutation pattern and can be treated as the enlargements of the Poincaré or Anti-de-Sitter (super)algebras. Obtained superalgebras are rooted in the Semigroup expansion method and Maxwell and Soroka–Soroka algebras, spanned by the Lorentz generator Jab, translations Pa, and additional Lorentz-like generator Zab. Considered configurations include cases up to two fermionic supercharges Qα and offer interesting modifications to the gauge (super)gravity theories.
Recommended citation: R. Durka, K. M. Graczyk, Acta Phys.Polon.Supp. 16 (2023) 6, 11 https://www.actaphys.uj.edu.pl/fulltext?series=Sup&vol=16&aid=6-A11
Published in Scientific Reports, 2023
We adopt convolutional neural networks (CNN) to predict the basic properties of the porous media. Two different media types are considered: one mimics the sand packings, and the other mimics the systems derived from the extracellular space of biological tissues. The Lattice Boltzmann Method is used to obtain the labeled data necessary for performing supervised learning. We distinguish two tasks. In the first, networks based on the analysis of the system’s geometry predict porosity and effective diffusion coefficient. In the second, networks reconstruct the concentration map. In the first task, we propose two types of CNN models: the C-Net and the encoder part of the U-Net. Both networks are modified by adding a self-normalization module [Graczyk et al. in Sci Rep 12, 10583 (2022)]. The models predict with reasonable accuracy but only within the data type, they are trained on. For instance, the model trained on sand packings-like samples overshoots or undershoots for biological-like samples. In the second task, we propose the usage of the U-Net architecture. It accurately reconstructs the concentration fields. In contrast to the first task, the network trained on one data type works well for the other. For instance, the model trained on sand packings-like samples works perfectly on biological-like samples. Eventually, for both types of the data, we fit exponents in the Archie’s law to find tortuosity that is used to describe the dependence of the effective diffusion on porosity.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Dawid Strzelczyk, Maciej Matyka, Sci Rep 13, 9769 (2023) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-36466-w
Published in arxiv, 2023
Physics informed neural network (PINN) approach in Bayesian formulation is presented. We adopt the Bayesian neural network framework formulated by MacKay (Neural Computation 4 (3) (1992) 448). The posterior densities are obtained from Laplace approximation. For each model (fit), the so-called evidence is computed. It is a measure that classifies the hypothesis. The most optimal solution has the maximal value of the evidence. The Bayesian framework allows us to control the impact of the boundary contribution to the total loss. Indeed, the relative weights of loss components are fine-tuned by the Bayesian algorithm. We solve heat, wave, and Burgers equations. The obtained results are in good agreement with the exact solutions. All solutions are provided with the uncertainties computed within the Bayesian framework.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Kornel Witkowski, arxiv:2308.13222 https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.13222
Published in Physical Review D, 2023
The elastic and inelastic neutral current Nu (Anit Nu) scattering off the polarized nucleon is discussed. The inelastic scattering concerns the single-pion production process. We show that the spin asymmetries measurement can help to distinguish between neutrino and antineutrino neutral current scattering processes. The spin asymmetries also encode information about a type of target. Eventually, detailed studies of the inelastic spin asymmetries can improve understanding of the resonant-nonresonant pion production mechanism.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Beata E. Kowal, Phys.Rev.D 108, 093002 (2023) https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.108.093002
Published in Physical Review D, 2024
The Short-Baseline Neutrino program in Fermilab aims to resolve the nature of the low-energy excess events observed in LSND and MiniBooNE, and analyze with unprecedented precision neutrino interactions with argon. These studies require a reliable estimate of neutrino cross sections, in particular for charged current quasielastic scattering (CCQE). Here, we report updates of the nuwro Monte Carlo generator that, most notably, bring the state-of-the-art spectral functions to model the ground state properties of the argon nucleus, and improve the accuracy of the cross sections at low energies by accounting for the effects of the nuclear Coulomb potential. We discuss these developments in the context of electron and neutrino interactions, by comparing updated nuwro predictions to experimental data from Jefferson Laboratory Hall A and MicroBooNE. The MicroBooNE CCQE-dominated data are described with the χ2 per degree of freedom of 0.7, compared with 1.0 in the local Fermi gas model. The largest improvement is observed for the angular distributions of the produced protons, where the χ2 reduces nearly by half. Being obtained using the axial form factor parametrization from MINERvA, our results indicate a consistency between the CCQE measurements in MINERvA and MicroBooNE.
Recommended citation: Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Artur M. Ankowski, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Beata E. Kowal, Hemant Prasad, Jan T. Sobczyk, Phys. Rev. D 109, 073004 https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.109.073004
Published in Physical Review C, 2024
Employing the neural network framework, we obtain empirical fits to the electron-scattering cross sections for carbon over a broad kinematic region, extending from the quasielastic peak through resonance excitation to the onset of deep-inelastic scattering. We consider two different methods of obtaining such model-independent parametrizations and the corresponding uncertainties: based on the bootstrap approach and the Monte Carlo dropout approach. In our analysis, the 𝜒2 defines the loss function, including point-to-point and normalization uncertainties for each independent set of measurements. Our statistical approaches lead to fits of comparable quality and similar uncertainties of the order of 7%. To test these models, we compare their predictions to test datasets excluded from the training process and theoretical predictions obtained within the spectral function approach. The predictions of both models agree with experimental measurements and theoretical calculations. We also perform a comparison to a dataset lying beyond the covered kinematic region, and find that the bootstrap approach shows better interpolation and extrapolation abilities than the one based on the dropout algorithm.
Recommended citation: Beata E. Kowal, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Artur M. Ankowski, Hemant Prasad, Jan T. Sobczyk, Phys. Rev. C 110, 025501 https://journals.aps.org/prc/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevC.110.025501
Published in Contributions to the Proceedings of the 25th International Workshop on Neutrinos from Accelerators, 2025
In this article, we highlight physics improvements in the NuWro Monte Carlo event generator. The upcoming version of NuWro will incorporate the integration of the argon spectral function for quasi-elastic scattering, along with the MINERνA parametrization of the axial form factor. Additionally, the new release will feature the implementation of the Valencia 2020 model for meson exchange current. The previously used simplistic delta resonance model for single-pion production will be replaced by a more accurate Ghent hybrid model in the upcoming version of NuWro. We also discuss the recent advancements made by the Wroclaw Neutrino Group in applying machine-learning techniques to achieve model-independent reconstruction of lepton-nucleus interactions
Recommended citation: Hemant Prasad, Jan T. Sobczyk, Artur M. Ankowski, J. Luis Bonilla, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Beata E. Kowal, arXiv:2501.11470 https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.11470
Published in Physical Review D, 2025
We present the implementation and results of a new model for the 𝑛-particle 𝑛-hole (np-nh) contribution in the NuWro event generator, grounded in the theoretical framework established by the Valencia group in 2020. For the 2p2h component, we introduce a novel nucleon sampling function with tunable parameters to approximate correlations in the momenta of outgoing nucleons. These parameters are calibrated by comparing our results to those of the Valencia model across a range of incoming neutrino energies. In addition, our model incorporates a distinct contribution from the 3p3h mechanism. We discuss the differences between the new NuWro implementation, the original Valencia model, and the previous NuWro version, focusing on the distribution of outgoing nucleon momenta. Finally, we assess the impact of the hadronic model on experimental analyses involving hadronic observables.
Recommended citation: Hemant Prasad, Jan T. Sobczyk, Artur M. Ankowski, J. Luis Bonilla, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Beata E. Kowal, Phys. Rev. D 111, 036032 https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.111.036032
Published in Physical Review D, 2025
We propose a new approach to simulate neutrino scattering events as an alternative to the standard Monte Carlo generator approach. Generative adversarial neural network (GAN) models are developed to simulate charged current neutrino-carbon collisions in the few-GeV energy range. We consider a simplified framework to generate muon kinematic variables, specifically its energy and scattering angle. GAN models are trained on simulation data from nuwro Monte Carlo event generator. Two GAN models have been obtained: one simulating quasielastic neutrino-nucleus scatterings and another simulating all interactions at given neutrino energy. The models work for neutrino energy ranging from 300 MeV to 10 GeV. The performance of both models has been assessed using two statistical metrics. It is shown that both GAN models successfully reproduce the distribution of muon kinematics.
Recommended citation: Jose L. Bonilla, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Artur M. Ankowski, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Beata E. Kowal, Hemant Prasad, Jan T. Sobczyk, Phys. Rev. D112, 013007 (2025) https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/l6td-93sr
Published in Physical Review Letters, 2025
Transfer learning allows a deep neural network (DNN) trained on one type of data to be adapted for new problems with limited information. We propose to use the transfer learning technique in physics. The DNN learns the details of one process, and after fine-tuning, it makes predictions for related processes. We consider the DNNs, trained on inclusive electron-carbon scattering data, and show that after fine-tuning, they accurately predict cross sections for electron interactions with nuclear targets ranging from helium-3 to iron.
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Beata E. Kowal, Artur M. Ankowski, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Jose Luis Bonilla, Hemant Prasad, Jan T. Sobczyk, Phys. Rev. Lett. 135, 052502 (2025) https://doi.org/10.1103/zxv6-22tz
Published in arXiv, 2025
Neutrino-oscillation experiments performed in the few-GeV energy region create an urgent demand for a significant improvement in the accuracy of modeling of neutrino interactions with atomic nuclei. Here, we report an updated implementation of the spectral function approach in the \nuwro{} Monte Carlo generator, which consistently treats multinucleon final-states in quasielastic scattering at the inclusive and exclusive level. After validating its accuracy against inclusive electron-scattering data, we compare its predictions to various neutrino cross sections from MicroBooNE. We find that with the multinucleon contribution, these data are reproduced with χ2 per degree of freedom of 1.3–1.8, compared to 2.7–7.2 without it.
Recommended citation: Artur M. Ankowski, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Jan T. Sobczyk, José L. Bonilla, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Beata E. Kowal, Hemant Prasad, arXiv:2508.10101 https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10101
Published in Physical Review D, 2025
We utilize transfer learning to extrapolate the physics knowledge encoded in a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) model trained on synthetic charged-current (CC) neutrino-carbon inclusive scattering data. This base model is adapted to generate CC inclusive scattering events (lepton kinematics only) for neutrino-argon and antineutrino-carbon interactions. Furthermore, we assess the effectiveness of transfer learning in re-optimizing a custom model when new data comes from a different neutrino-nucleus interaction model. Our results demonstrate that transfer learning significantly outperforms training generative models from scratch. To study this, we consider two training data sets: one with 10,000 and another with 100,000 events. The models obtained via transfer learning perform well even with smaller training data. The proposed method provides a promising approach for constructing neutrino scattering event generators in scenarios where experimental data is sparse.
Recommended citation: José L. Bonilla, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Artur M. Ankowski, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Jan T. Sobczyk, Beata E. Kowal, Hemant Prasad, arXiv:2508.12987 https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.12987
Published in Physical Review C, 2025
We present an updated deep neural network model for inclusive electron-carbon scattering. Using the bootstrap model [Phys.Rev.C 110 (2024) 2, 025501] as a prior, we incorporate recent experimental data, as well as older measurements in the deep inelastic scattering region, to derive a re-optimized posterior model. We examine the impact of these new inputs on model predictions and associated uncertainties. Finally, we evaluate the resulting cross-section predictions in the kinematic range relevant to the Hyper-Kamiokande and DUNE experiments.
Recommended citation: Beata E. Kowal, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Artur M. Ankowski, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, Jose L. Bonilla, Hemant Prasad, Jan T. Sobczyk, Phys. Rev. C 112, 055504 https://journals.aps.org/prc/abstract/10.1103/ydvc-2567
Published in arXiv, 2025
Recent experimental data from MINERvA on transverse kinematics observables across four different nuclear targets - carbon, oxygen, iron, and lead - have been utilized to refine the modeling of final state interaction effects in the NuWro Monte Carlo neutrino event generator. For this purpose, we have developed an event reweighting tool for future applications to adjust the strength of final-state interactions. This study highlights the requirement for stronger nucleon reinteractions than previously assumed, but it still falls within the uncertainty range observed in a study comparing proton transparency measurements. This conclusion has significant implications for both experimental and theoretical work involving NuWro.
Recommended citation: Hemant Prasad, Jan T. Sobczyk, Rwik Dharmapal Banerjee, J. Luis Bonilla, Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Beata E. Kowal, Artur M. Ankowski, arXiv:2512.23350 https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.23350
Published in Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Wrocławskiego, 2025
Recommended citation: Krzysztof M. Graczyk, Maciej Matyka, Głębokie sieci neuronowe dla fizyki. W: Dariusz BURACZEWSKI, Małgorzata BIERNACKA, Paweł RYCHLIKOWSKI (red.), BadAI. Nauka w erze sztucznej inteligencji. Wrocław: Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Wrocławskiego, 2025, p. 35–54 https://wuwr.eu/produkt/badai-nauka-w-erze-sztucznej-inteligencji/
Published:
Published:
27th International Workshop on Nuclear Theory Rila Mountains
Published:
Published:
Published:
Nu-Physics and Machine Learning Lightning Talks Neutrino 2020 Satelite Workshop
Published:
Published:
Published:
Published:
Saxony meets Lower Silesia - Science Across Borders Conference
Published:
Graduate course, Wroclaw University, Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, 2014
Elements of lepton-nucleon electromagnetic interactions
Undergraduate and graduate course, Wroclaw University, Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, 2019
It was an introduction to neural computations. The course covers:
Undergraduate and graduate course, Wroclaw University, Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, 2020
Overview of application of deep learning in physics
Undergraduate and graduate course, Wroclaw University, Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, 2021
It was a short introduction to neural networks (10h of lecture and 10h of labs). The course consists of:
Graduate course, Wroclaw University, Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, 2021
Introduction to theory of elementary particles (30h of lecture and 30h of classes). The course consists of:
Undergraduate course, Wroclaw University, Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, 2021
Numeric and symbolic computations in Wolfram Mathematica.
Undergraduate and graduate course, Wroclaw University, Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, 2022
Short introduction to Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINN)
Undergraduate course, Wroclaw University, Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, 2023
Deep Learning in five steps.